Start accessing your command line server or desktop by installing Cockpit on Debian 12 Bookworm or 11 Bullseye using this tutorial’s given terminal commands.
Managing a Linux server with a Command line interface remotely will be difficult if you don’t have prior knowledge of Linux commands. But this can be easy if we are using the COCKPIT server management tool. It is a lightweight application tool that offers a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) to manage Linux servers or desktops remotely.
The cockpit is open source and allows admins to monitor system resources, create Podman containers, manage user accounts, issue commands, configure network settings, view system logs, and perform other administrative tasks. It is quite a useful tool for both novice and experienced administrators and the best part is it can be installed on almost all popular Linux distributions and can be accessed from any modern web browser, including mobile devices.
One of the best features of Cockpit is users can manage multiple Linux servers from its single web interface. Hence, it helps admins to save a lot of time if there are multiple servers that need to be managed and monitor.
Steps to configure Cockpit on Debian 12 or 11 Linux
1. Visit Command Terminal
If you want to install Cockpit on some remote Debian server, then access it using SSH, whereas the local system users can directly open the command terminal.
2. Update the Package List
Once you are on the terminal of Debian, the next task is to perform the system update command, so that our system has the latest security updates and up-to-date APT package list.
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgrade3. Installing Cockpit on Debian 12 or 11
The cockpit is a quite common application or package that is available through the default repositories of most of the Linux distros including Debian. So, on your command terminal, simply use the APT package manager and install it.
sudo apt install cockpit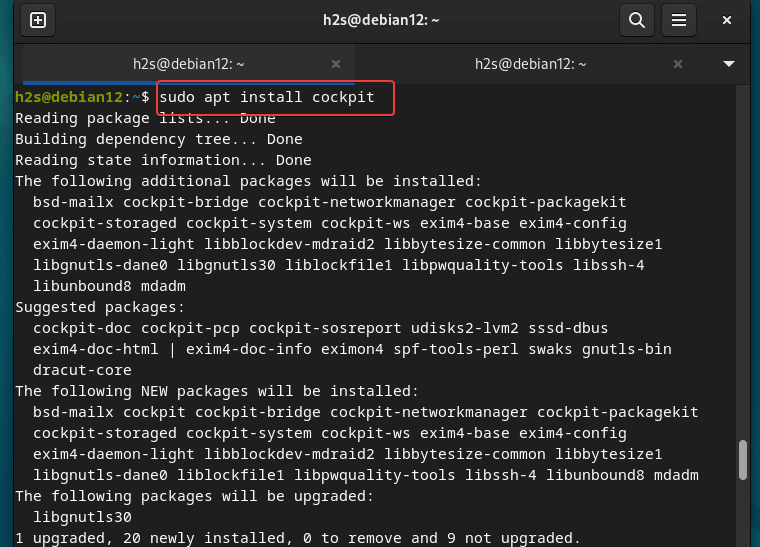
4. Access Cockpit Web interface
Once the installation is completed, open the browser that can access the IP address or domain where you have installed the Cockpit. However, don’t forget to open port number 9090 if you have an active firewall.
In the browser URL type- https://server-ip-address:9090
Replace server-ip-address with the actual address.
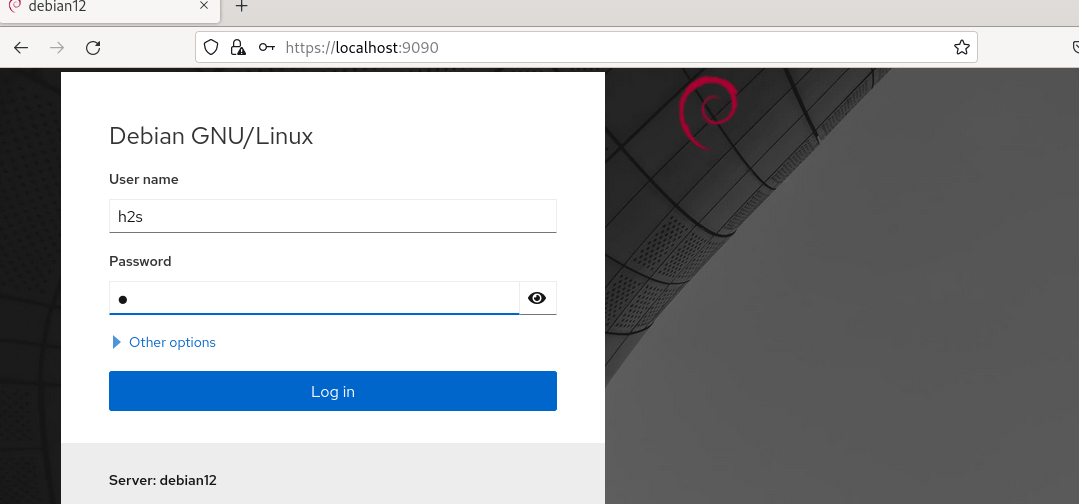
5. Login with your Debian username
Now, in the Cockpit login interface, you can use whatever user you have on Debian to log in. For full control, you can use root or sudo user.
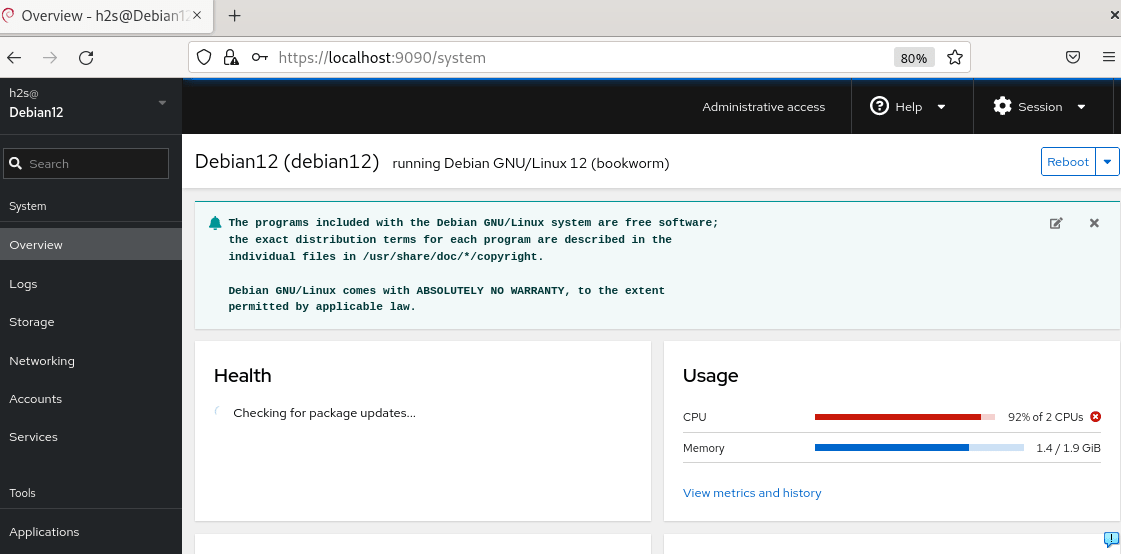
6. Cockpit Dashboard on Debian 11 | 12
Now, you will have the Dashboard of Cockpit with various settings and real-time system monitoring values. You can keep your eye from here on how much load is on your system.
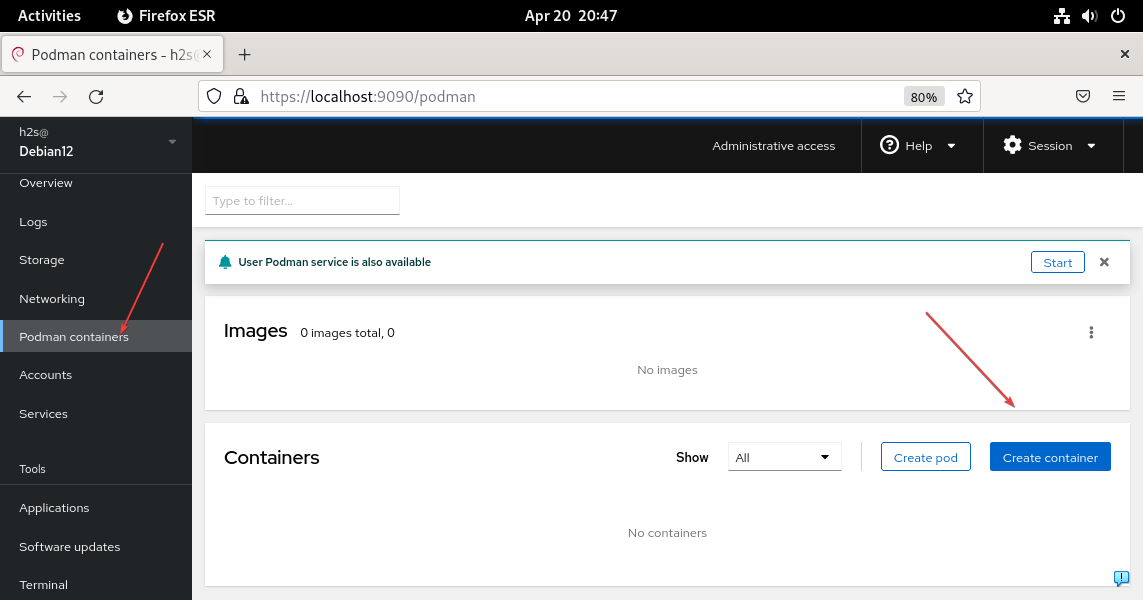
7. Podman for Cockpit to run containers
If you also want to create and run containers using the interface of Cockpit then that is possible as well. For that on your command terminal install the cockpit-podman package.
sudo apt install cockpit-podmanOnce the installation is completed, go to the Dashboard and there you will see the Podman Containers option.
8. Updates and Uninstallation
The future updates for the Cockpit will automatically get installed as you run the system update and upgrade command i.e
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeHowever, those who in future don’t want Cockpit anymore on their Debian 12 or 11 Linux, can run the uninstallation command:
sudo apt autoremove cockpit*The default port number used by the Cockpit is port – 9090, we can use it along with the server ip-address to access the Dashboard.
No, Cockpit is a server management tool that offers a web-based interface for easily managing remote or local Linux servers.
Instead of docker, by default Cockpit offers docker-compatible Podman to create containers using the web interface.
Other Articles:
Thanks for the article, but note that Cockpit does not work 100% on Debian or Ubuntu.
Cockpit on Debian or Ubuntu servers with systemd-networkd instead of network-manager will not have the ability to manage the network or anything related to networking. Cockpit is only fully functional on Debian-like distros that have networkmanager enabled – this usually means desktop installs, not servers.
What desktop install will provide the needed networkmanager? There are many GUI install choices.
Does this mean Gnome must be installed to get network management in cockpit?
No there is no need to have GUI on Linux to manage network using Cockpit