It is not very difficult to find some best alternative to Gnome system monitor application that comes out of the box with Gnome desktop environments such as in Ubuntu operating systems. Hence, here are some…
In Windows to measure system performance, we use the Task Manager application, well in Linux we can do precisely the same either using various GUI, web-based system monitor applications, or simply via Command-line tools. It just like a Car Dashboard where we have all information on the status of the engine, fuel, speed, and other things.
Similarly, if we have a machine running on Linux and to get an idea about the system load, the network interface, and the temperatures of the processor and chipset; what hardware is actually in the system? We can use Task Managers and process viewers.
We need answers to this question not only just to find out the Linux system performance in everyday life but also sometimes to look at the hardware and its utilization to know where a bottleneck might occur. The diagnostic logs of hard drives and the system temperatures also allow an assessment of the system’s health.
Gnome system monitor alternative apps for Linux
Tools to check out Linux hardware performance presented in the below list contains both GUI and CLI (command line) ones for the terminal to provide detailed hardware and performance data in text mode or graphically. Of course, GUI is a good option, however, systems such as server and mini-PCs like Raspberry pi which often do not use a graphical user interface and are only managed via SSH access on the command line, text-based system monitor tools are great options such as htop. Moreover, Gnome system monitor similar tools given here are not just limited to Ubuntu, Debian, or Linux Mint, the users can install and use them in CentOS, Manjaro, Fedora, and other popular Linux distros.
1. Stacer – Linux system optimizer and application monitor
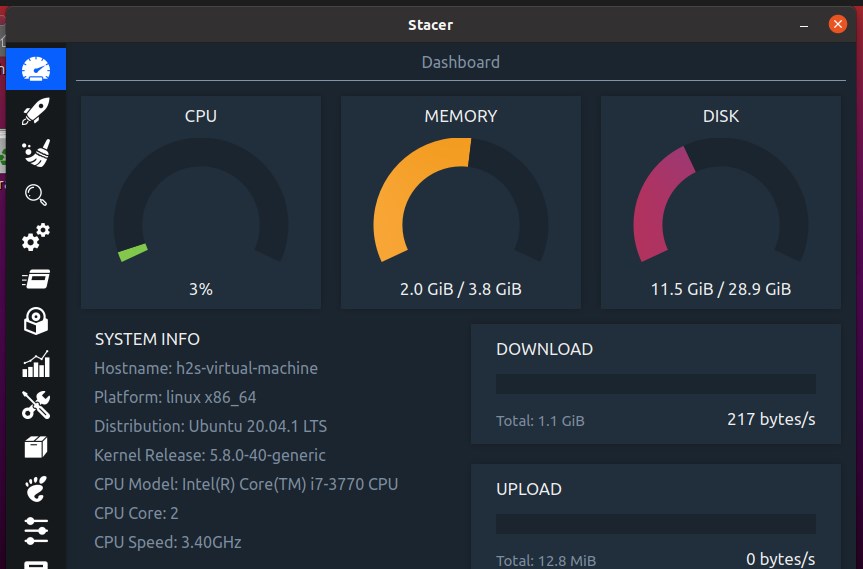
Stacer which is also an open-source application can be considered as one of the best Gnome system monitor alternative tools in the GUI category. Because it has a beautiful and interactive interface to give the whole system performance metrics in one place. The best thing about Stacer, it is not just limited to showing process or work as a task manager on Linux, it can further use to optimize the Linux systems, just like we have CCleaner for Windows PC and laptops.
It features Startup Apps manager, a tab on the Stacer from where the users can take a view of the apps that are set to launch with the boot, and even gives the option to set new startup apps. This removes the headache of beginners to mingle with commands to tell the system which application needs to be started automatically on the next machine boot.
Stacer System cleaner option lets users quickly clear all unnecessary logs, cache files, and even empty Trash bin on Linux system with just a few clicks.
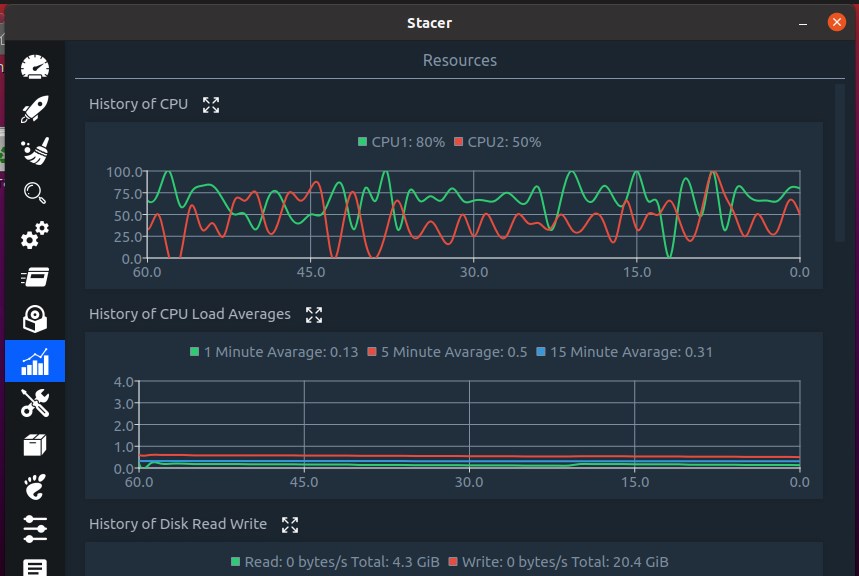
Apart from this, managing of starting and stopping system services; sorting and searching of process sorted by PID, CPU and memory usage, etc.; one-click option to uninstall and remove installed software or packages; Snap package uninstaller; resources tab to view CPU, RAM, Disk, CPU Load Average and network activity usage along with the graph; APT – Repository Manager to enable or disable added system repository with just one click.
Stacer is available for both Debian and RPM-based systems, whereas its AppImage package enables users to install Stacer on any popular Linux distro.
To install Stacer on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, use these commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oguzhaninan/stacer sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install stacer
Well, other Linux platform users can see the Stacer Github page for RPM and AppImage.
2. htop – Linux process and resource viewer
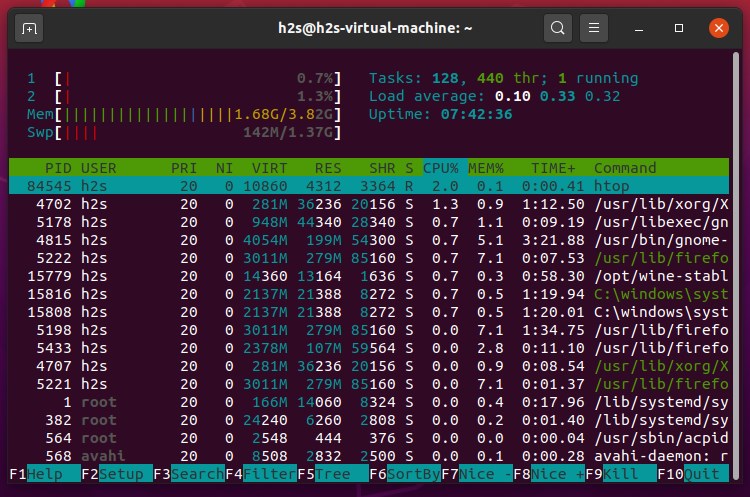
Those who don’t want an interactive text-based alternative to the Gnome system monitor and Top tool, then try out htop. It is a good option not only for Desktop but also in command line servers to check out system performance and view Linux process directly in Terminal.
It is an extended Linux task manager and system monitor that not only offers color and a more understandable structure but also shows the utilization of CPU, RAM, and swap partition in bars.
When we run it, htop turn our terminal screen into an informative area in which the lower part is filled with program and process list, which we can scroll through with the arrow keys. Whereas the top area shows cumulative info about memory, Swap, CPU usage, and more.
As it uses text mode to show Linux process thus on it we can use keyboard shortcuts such as F3 your search in the process list, with F9 you can send stop commands to hanging processes. F10 terminates the htop program.
The tool is available for all Linux distributions via the respective package manager for easy installation, under Ubuntu and Debian, we can use this command to install htop
sudo apt install htop
For Fedora & RHEL
dnf install htop
And to use it just type: htop in Terminal
3. xfce task manager
Xfce Task Manager is another graphical user interface Linux process and resource viewer application that can be easily installed on Linux systems.
This Gnome’s alternative task manager and system monitoring program is light in weight and similar in appearance to the Gnome system monitor tool. After the installation, you will see the upper portion of the program showing the CPU and Memory usage in a graph including several processes a SWAP usage percentage.
Apart from this, we can easily stop, terminate, kill or change the priority of any process by right-clicking on a process that brings up a menu directly on the Xfce task manager interface.
To install Xfce on Ubuntu or Debian based Linux run:
sudo apt update sudo apt install xfce4-taskmanager
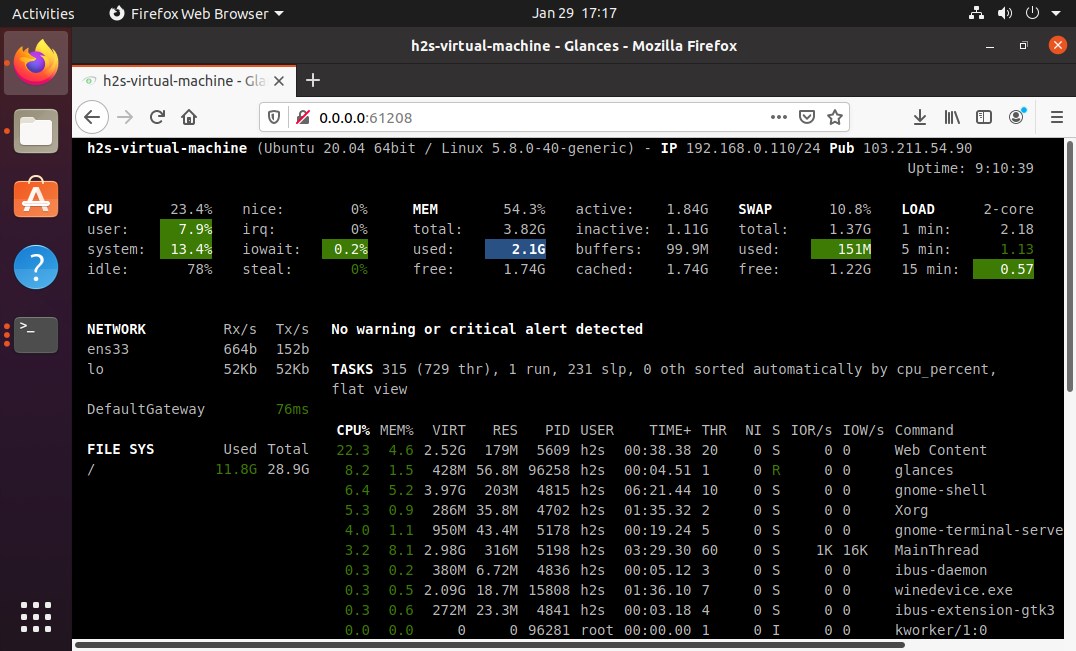
4. Glances system monitoring with web interface
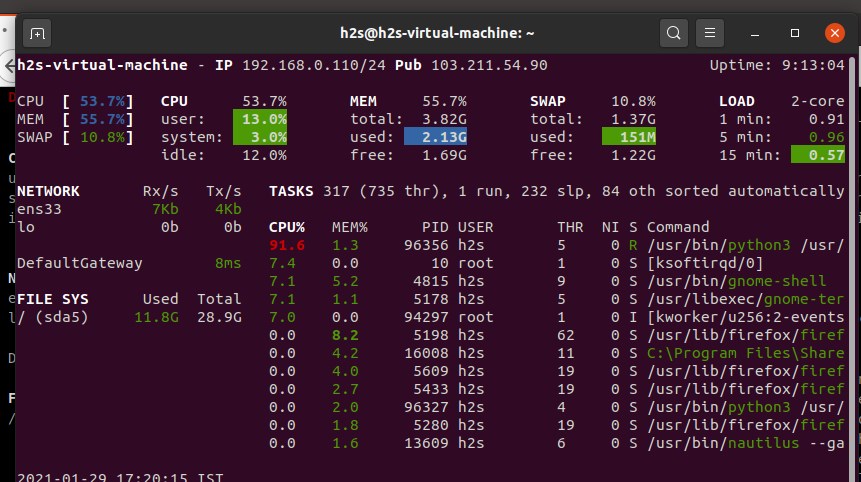
‘Glances’ is the Linux monitoring system that comes with a web interface as well as a local terminal. Yes, just like htop given in this list of tools to replace the Gnome system monitoring tool, this one is also an interactive text-based performance monitoring tool that can also be viewed in a browser.
It has been written in Python, thus, supports any major platform having python installed such as Windows, macOS, Linux, FreeBSD, and Android.
One can use its client-server model to monitor remote systems either using SSH, web interface, or API (XML-RPC and RESTful). Stats can also be exported to files or external time/value databases such as InfluxDB, Cassandra, CouchDB.
Although out-of-the-box Glances provides all necessary information about the system in which it has been installed, developers can extend its abilities by adding plugins or export modules.
Glances installation on Ubuntu or Debian
sudo apt install glances
Whereas other Linux, Windows, macOS, and Android users can see the Glances Github page for more info.
To run it, just type- glances in terminal to get a web interface type glances -w and on the web browser type the IP address along with the port given in the command output.
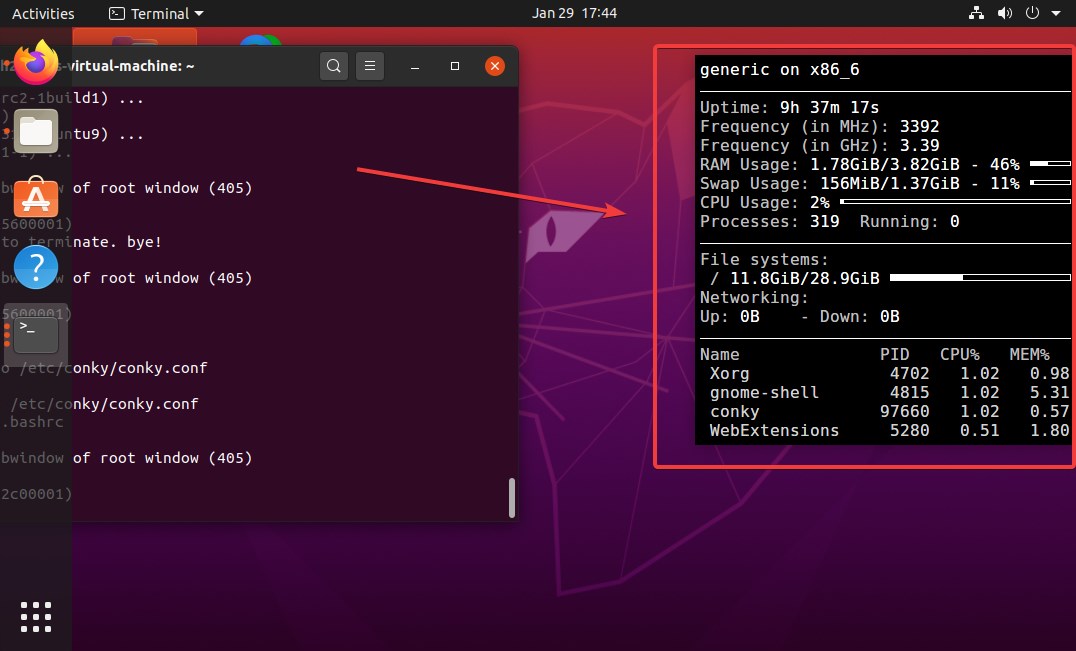
5. Conky system monitor
Conky system monitor is a nice option for those who want a 24-hour view of the system process and resource via a desktop widget. It is an extremely lightweight Linux system monitoring tool and alternative for those who don’t want to open again and again Gnome system monitor to have a look at Linux system processes and resource consumption such as hard disk, memory, and CPU usage.
However, the Conky system monitor for Linux is for slightly advanced users, those who know how to deal with different command editings. Because to change the placement of the Conky widget and other customization, the user has to customize its configuration file.
Conky system monitor install on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04 or Debian:
sudo apt install conky-all
To run it type:
conky
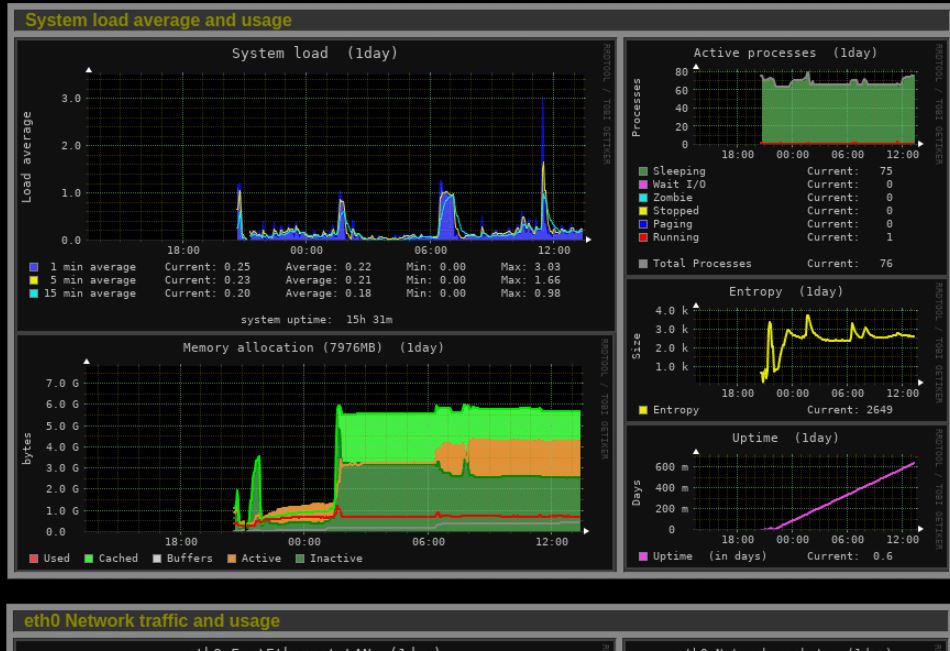
6. Monitorix- web interface Linux system monitor
After Glances, this one is another Gnome system monitor substitute that supports a web interface to give a view of the Linux process and hardware resources. Such monitoring software is a good option for command-line Linux servers, especially with a limited amount of hardware resources such as Raspberry pi. Monitorix can score where tools like Grafana or Munin are overdone.
Monitorix is written in Perl and comes with its own web server, which can be reached by default via port 8080 at http://localhost:8080/monitorix and can optionally be password- protected.
The installation is pretty easy for almost all popular Linux distros such as RHEL, Fedora, CentOS, Ubuntu, Arch, Manjaro, Debian, and more…
For RHEL based Linux with EPEL repo enabled – yum install monitorix
For Debian or Ubuntu-based Linux- sudo apt install monitorix
Being an open-source tool, the Monitorix source code is available on Github to follow and download. Also, since Buster, Monitorix has been included in the Debian package sources that’s why we can install it on Debian or Ubuntu without any third-party repo.
Yes, of course, it’s a reliable and fast monitoring tool that can be easily set up on the home server or Raspberry Pi. If you don’t trust the built-in web server, Monitorx can also be made accessible via one of the well-known web servers such as Apache and lighthttpd.
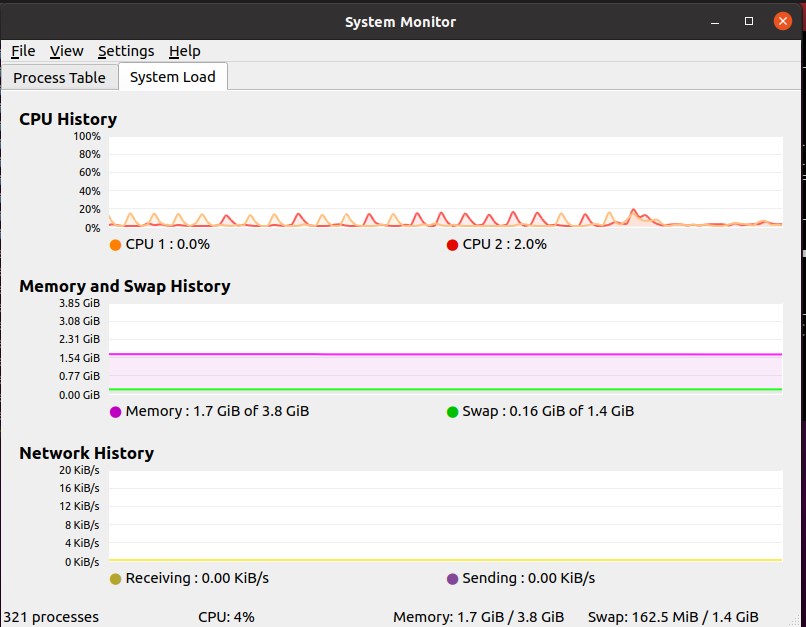
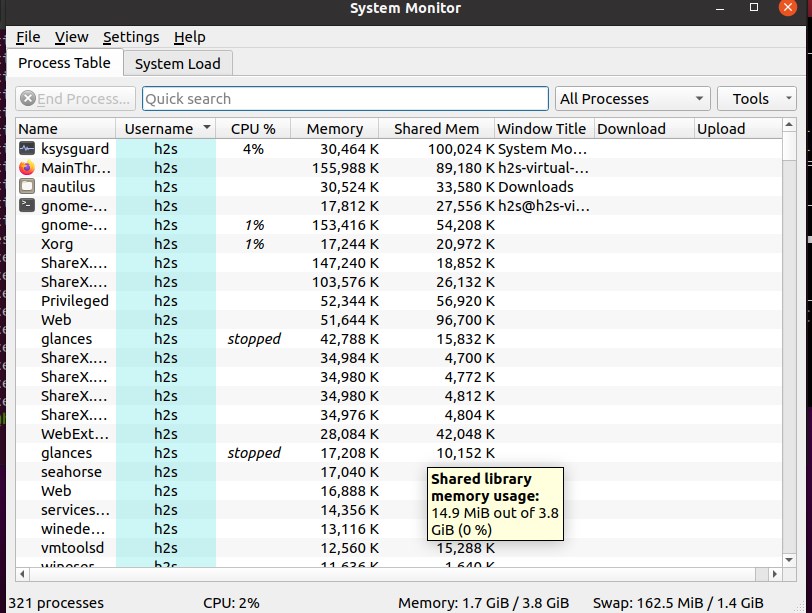
7. KDE System Guard- KSysGuard
KDE System Guard is the Linux task manager and performance monitor for the KDE platform. And of course, just like the Gnome system monitor, it is also not a very lightweight Linux process and hardware resource viewer as compared to few others mentioned in this list, however highly interactive. As we know KDE apps know for their good graphical user interface that makes anybody easily handle them. Thus, we don’t recommend it for servers or mini PCs instead modern Linux desktops and laptops can use it easily.
We can monitor local as well as remote hosts system using KSysGaurd, however, the remote system must have ksysguardd installed on the remote host.
It offers two tab view, one for resource graphs and the other dedicated to all Linux system process.
Other Articles:
- How to install Open Hardware Monitor Linux on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- 10 Best software to monitor CPU Core Temperature for Windows
- List of Best SQL Server Monitoring Tools
- 9 Best Open source Network Monitoring Tools



btop (or bpytop), best console tool with graphs