MongoDB doesn’t need an introduction, the one who is system administrating and developing would already know about it. It is a NoSQL database available to install on popular operating systems to provide a database without a fixed structure, hence easily scalable. Here in this article, we will learn the steps to easily install or create a MongoDB Database server container on the Docker Engine platform.
What do we need to perform in this tutorial?
- A system with Docker
- Access to its command line
- Internet connection
Steps to install MongoDB & Mongo Express on Docker
Make sure you have Docker
The first thing I am assuming is that you already have Docker installed on your system. If not then as per your operating system go through the below-given tutorials and set up the one for you.
• How to install and setup Docker Container on AlmaLinux 8
• Install and setup Docker Container on Rocky Linux 8 or CentOS/RHEL 8
• Install Docker CE on Debian 11 Bullseye Linux
• Best way to install Docker on Ubuntu 20.04…
• How to install Docker on Windows 10
Download or Pull MongoDB Docker Image
The best thing that made Docker popular is its repository that holds hundreds of pre-built Images from official and non-official sources. We can use them to create containers instantly, yes, of course, MongoDB is also there. Hence, just on your machine run the Docker Pull command:
docker pull mongo
The above command will pull the latest version image on MongoDB Server on your Docker, however, for any other versions, you have to use the tag. For Example, docker pull mongo:4.4.9. For all available tags, you can see its Github page.
To check the downloaded image on the system, you can use:
docker images
Create MongoDB Database Server Container
We have already the image, now use it to create as many Database running containers as you want. However, before that let’s create a folder on our system to hold the databases data created on the MongoDB running container. As we know once we start using the Database server for commercial usage its data become valuable, but in case we need to delete the container in the future that process will also remove all of its data. Hence, to play safe let’s create a folder-
sudo mkdir /var/dbdata
Now, create Mongo Container:
docker run -it -d -v /var/dbdata:/data/db -p 27017:27017 --name mongodb mongo
Explanation of the above command:
/var/dbdata:/data/db – Assigning our created folder to use for storing MongoDB data.
-p 27017:27017 : Opening Database server container port to access from the host system.
--name MongoDB : Giving some name to our container
mongo : It is the name of the downloaded Image file
Start container:
docker start mongodb
Access MongoDB Database Docker Terminal (Bash Shell)
Now, if you want to access the command line of the Mongo server to create databases and manage them, here is the command:
sudo docker exec -it mongodb bash
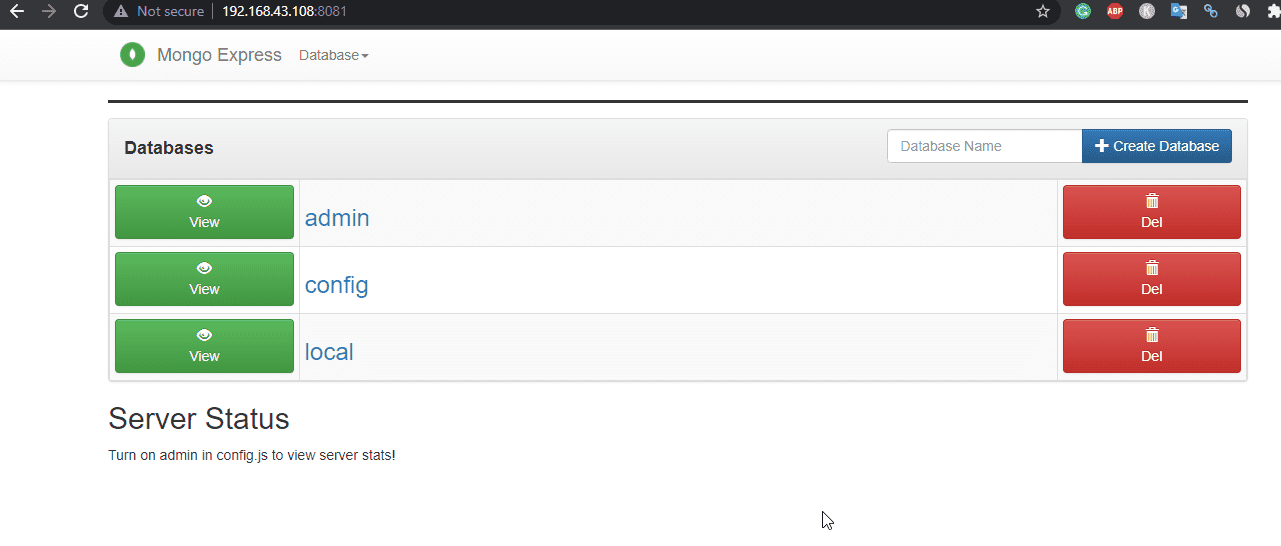
Create Mongo Express Web Interface container (optional)
Well, those who want a web-based graphical user interface to manage their Docker MongoDB server databases, can go for the further installation of Mongo Express by creating a container.
Note: JSON documents are parsed through a javascript virtual machine, so the web interface can be used for executing malicious javascript on a server. mongo-express should only be used privately for development purposes.
docker run --link mongo_db_name_container:mongo -p 8081:8081 -e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_URL="mongodb://mongo:27017" mongo-express
Link your Docker running MongoDB server with Express, by replacing the above “mongo_db_name_container” in the above command.
For example, here we have created a database container with the name- mongodb hence the above command will be:
docker run --link mongodb:mongo -p 8081:8081 -e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_URL="mongodb://mongo:27017" mongo-express
To access the web interface, open your browser and type: http://localhost:8081