Podman is promoted as an alternative to Docker that advertises as a tool compatible with Docker Images. Also, it offers a command line that is identical to Docker and is intended to simplify the migration from Docker to Podman for both users and programs. Under the hood, however, the two container tools are very different. Podman is a daemon-less tool instead it uses a runC container runtime process whereas Docker uses a daemon to manage all resources.
Developed by Redhat, this container tool was originally planned as a debugging tool for the CRI-O container engine, which specializes in Kubernetes, to simplify certain tasks for application developers and administrators of Kubernetes clusters. Since then, however, Podman has grown into a comprehensive tool for container management. Developers can easily install it from major software sources in Linux distributions such as Fedora, Arch Linux, and openSUSE Tumbleweed.
Here we learn the steps to install and use Podman on Rocky Linux 8 or AlmaLinux 8 using a command terminal to manage containers.
Run Containers using Podman on AlmaLinux 8 or Rocky Linux 8
To get a graphical user interface to manage Podman containers and servers, use the enable pre-installed Cockpit Web console on Rocky or AlmaLinux.
DNF update command
To ensure all the packages available on your Rocky or AlmaLinux 8 are up to date run the system update command.
sudo dnf update
Install Podman Container manager
The packages to install Podman are available via the default system repository of these two RHEL-based Linux operating systems. Hence, just use the DNF package manager to install this Podman.
sudo dnf install podman
Get Podman Compose on Rocky or AlmaLinux 8
Well, those who want to use Docker Compose implementation with Podman backend to make it run docker-compose.yml unmodified and rootless or create a new one can use the given command. In short, it is a drop-in replacement for docker-compose.
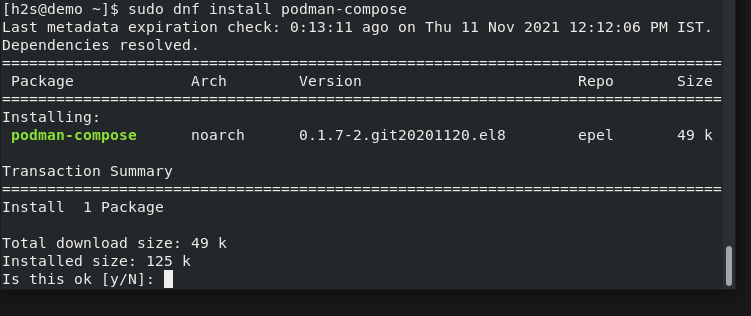
sudo dnf install podman-compose
Check Version and Start and Enable Service
Once the installation is completed to check which version of Podman you have and whether its service running without any error.
podman --version
Well, we can use Podman without running it as a service; via Socket. However, it also offers integration with Systemd services so containers or pods can be started at system boot and managed similarly to other services that may run on the host system.
If you want to start and enable Containers services with systemd then here are the commands to first enable the same for Podman.
sudo systemctl start podman sudo systemctl enable podman
Check Status:
systemctl status podman
View Podman system information
To get the system information using it, run:
podman info
Emulate Docker CLI using Podman (optional)
To use docker as a command tool instead of Podman. This means you can use the familiar docker command while underlying Podman will be executing.
sudo dnf install podman-docker
After that:
podman -v or docker -v
will give you the same result
Pull Docker Images and Create Containers
The good thing is we can directly pull the Images of various Apps available to create Containers in the Docker Hub library using Podman. Also, having an identical command line, it is easy for existing Docker users to manage Podman-created containers.
To search and pull any Image, let’s say Ubuntu
podman search ubuntu
And to pull/download
podman pull ubuntu
For creating a container using the downloaded image, use:
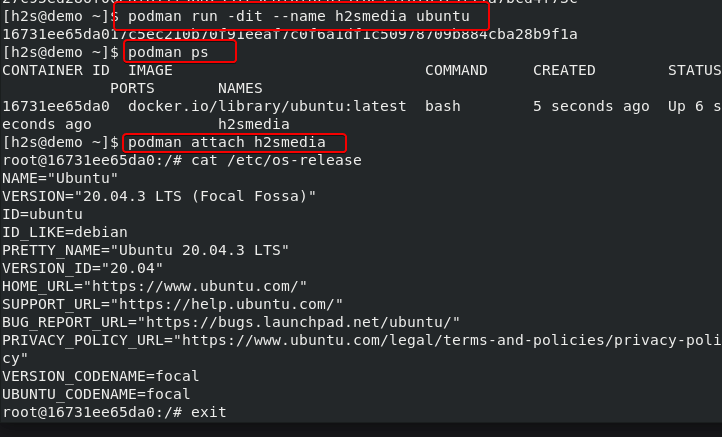
podman run -dit --name h2smedia ubuntu
h2smedia is the name of the container we want to make whereas ubuntu is the Image name we have downloaded or pulled.
To List containers:
podman ps
To list all
podman ps -a
Get running container command-line access:
podman attach container-name
example:
podman attach h2smedia
To Delete or remove the container
In case you want to remove created container then run:
podman rm container-name
Example:
podman rm h2smedia
Learn more about the Podman command line on RedHat Page.


Hi!
There is a typo in the section called “Get Podman Compose on Rocky or AlmaLinux 8”.
It says: “sudo dnf podman-compse”
It should obviously say: “sudo dnf install podman-compose”
//daishan