Learn the steps to install TimeShift on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy JellyFish and Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa using the command terminal.
Linux system installation and setup is not a difficult task but if you are new to it then issuing any wrong command could cause some error that would be difficult for you to resolve. In such a case, if a person has a backup of the system then restoring it to the earlier point when everything was working is quite easy using TimeShift. Even an experienced user can use it to remove the headache of installing a Linux from scratch if something goes wrong.
What is Linux TimeShift Program?
Like Windows System Restore and macOS Time Machine, Linux also has a tool called “TimeShift”. We can easily install this Linux system restore or backup tool on Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Debian. The key task of the tool is to create snapshots of the Linux file system that restore a previous state when restored.
The user Linux backup tool only creates differential backups and use storage space sparingly. Recovery points share common, unmodified files so they are not saved multiple times. Nevertheless, each snapshot contains a complete backup set, which can also be searched with a file manager, since identical files are represented by hard links. The first backup point is always a complete backup of the system directories and is quite large at a few gigabytes.
TimeShift uses Rsync to work in the background quietly to take care of system files and leaves users’ personal files in their home directories untouched, but also backs up their configuration files. Restoring a previous system status does not overwrite any documents, but also restores user settings. Also, supports the BTRFS Snapshot mode.
Steps to install TimeShift on Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04 LTS Linux
The commands given here are also applicable for other Linux distros based on either Debian or Ubuntu such as Linux Mint, POP OS, MX Linux, Linux Mint, Elementary OS, and more…
1. Requirements
• Ubuntu or Debian Linux
• A non-root user with sudo rights
• Terminal Access
• Internet Connection
2. Run Apt update command
Well, it is not necessary to run the system update command, however, if you have not for a while then it is recommended. This helps the system rebuild the repository cache and identify what are the new versions of packages available to download.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
3. Install TimeShift on Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04
We don’t need to add any extra repository to install TimeShift because we already have its packages in our Ubuntu’s default system repo. Hence, simply use the APT package manager to install TimeShift.
sudo apt install timeshift
4. Run TimeShift Application
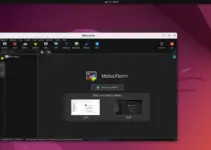
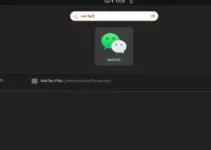
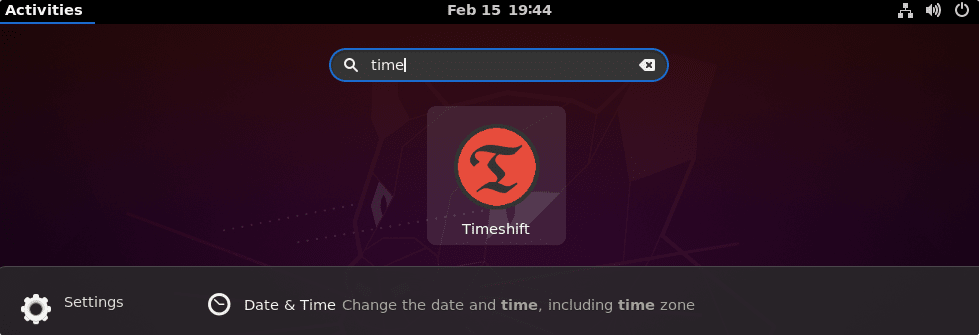
Once the installation is completed, go to Ubuntu’s Application launcher or whatever Debian-based system you are using. And search for “TimeShift“, as its icon appears, click to run the same.
To run it, the system will ask you to enter your user password.
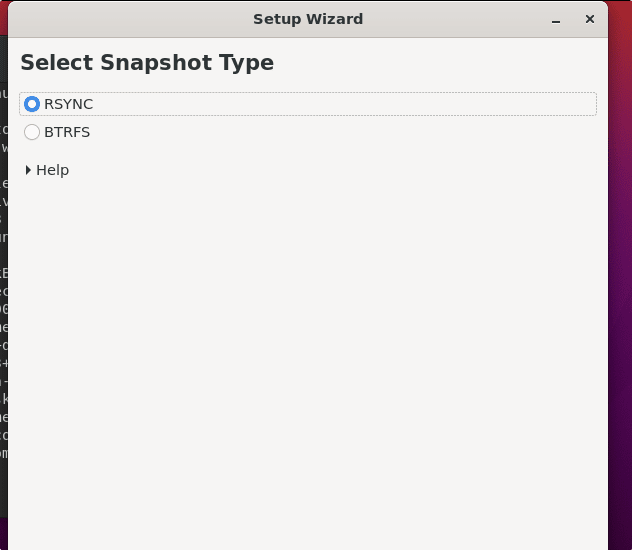
5. Select SnapShot Type
As this backup program is launched on your system, it will ask you to select the snapshot type between Rsync and BTRS. By default, Rsync will be selected. Go through the below-given details and select one of your choices.
Note: To use the BTRFS snapshot type your Linux file system must be formatted in BTRFS. Otherwise, go for rsync.
RSYNC Snapshots
• Snapshots are created by creating copies of system files using rsync, and hard-linking unchanged files from the previous snapshots.
• All files are copied when the first snapshot is created. Subsequent snapshots are incremental. Unchanged files will be hard-linked from the previous snapshot if available.
• Snapshots can be saved to any disk formatted with a Linux file system. Saving snapshots to non-system or external disks allows the system to be restored even if the system disk is damaged or re-formatted.
• Files and directories can be excluded to save disk space.
BTRFS snapshots
• Snapshots are created using the built-in features of the BTRFS file system.
• Snapshots are created and restored instantly. Snapshot creation is an atomic transaction at the file system level.
• Snapshots are restored by replacing system subvolumes. Since files are never copied, deleted, or overwritten, there is no risk of data loss. The existing system is preserved as a new snapshot after restore.
• Snapshots are perfect, byte-for-byte copies of the system. Nothing is excluded.
• Snapshots are saved on the same disk from which they are created (system disk). Storage on other disks is not supported. If the system disk fails then snapshots stored on it will be lost along with the system.
• Size of BTRFS snapshots is initially zero. As system files gradually change with time, data gets written to new data blocks which take up disk space (copy-on-write). Files in the snapshot continue to point to disk space (copy-on-write). Ales in the snapshot continue to point to original data blocks.
• OS must be installed on a BTRFS partition with Ubuntu-type subvolume layout (@ and @home subvolumes). Other layouts are not supported.
Know more about this tool at its GitHub Page.
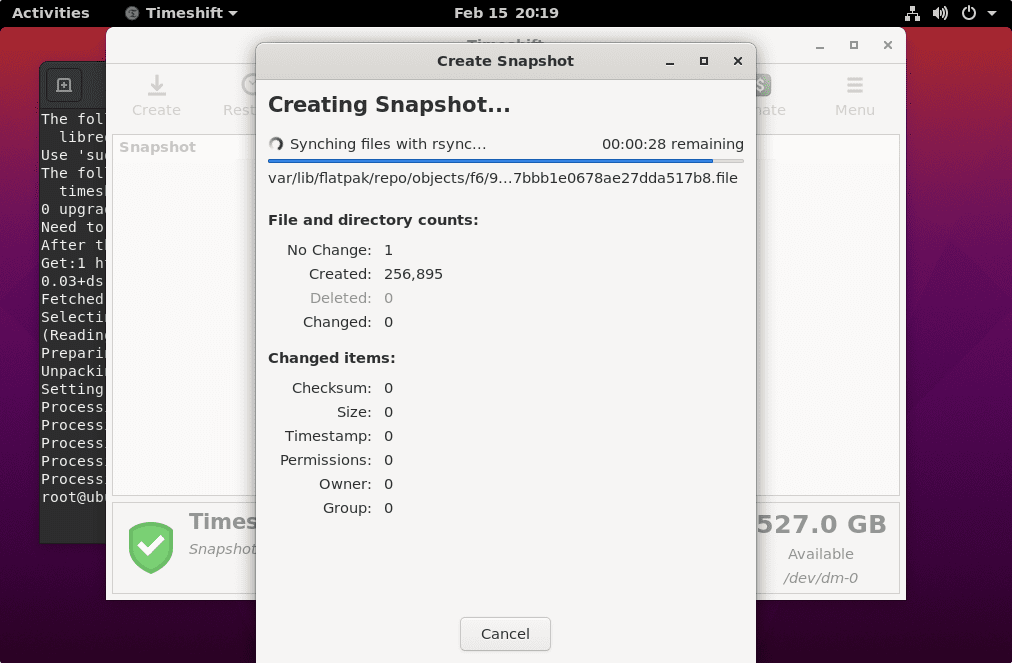
6. Create Ubuntu 22.04 or 20.04 Snapshot
Once you have the graphical user interface of the TimeShift, click on the “Create” button to start with your first system’s Snapshot.
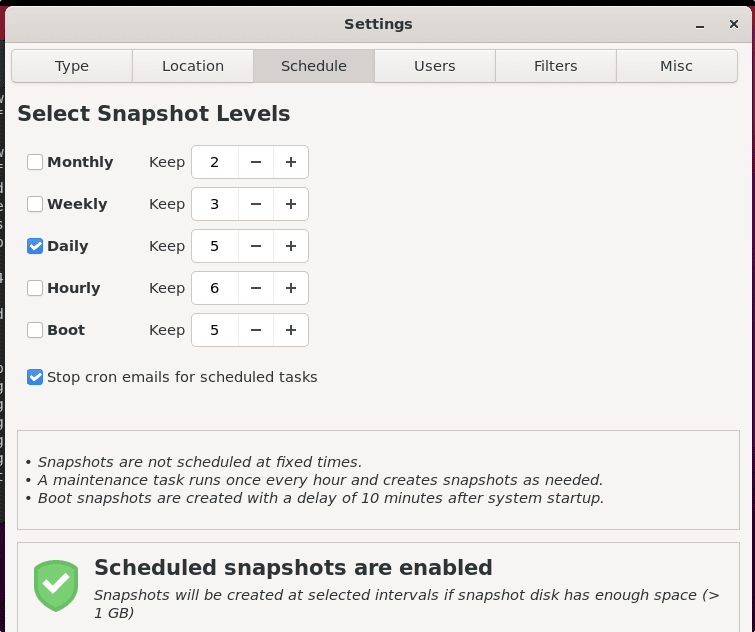
7. To schedule System backup
If you want the Timeshift to automatically take the system’s snapshot at some particular given time, then use the Schedule option of this tool.
• Click on the Setting option given in the Menu.
• Select Schedule Tab.
• Set the backup frequency you want.
8. How to update
Well, we have used the APT package manager and system’s default repository to install TimeShift, hence running the system update and upgrade command will also install if any latest version of TimeShift is available.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
9. Uninstall or Remove Timeshift
After some time, if you are not interested in the Timeshift anymore then we can remove it using the APT package manager and remove option. Here it is:
sudo apt remove timeshift -y
Other Articles:
• How to install Windows 11 on Ubuntu 20.04 using VirtualBox
• Command to take a backup of MySQL database table Structure
• How to Setup and use Google Drive on Ubuntu 20.04